en
names in breadcrumbs


Rupicapra is a genus of goat-antelope called the chamois. They belong to the bovine family of hoofed mammals, the Bovidae.
Two extant species are recognized.[1]
The Apennine chamois (Rupicapra pyrenaica ornata)[2] is a subspecies of the Pyrenean chamois, a goat-like mammal found in the mountains of Europe. Both male and female have hook-shaped horns that slightly curl backwards and grow little by little each year, never falling off. Their coats are light brown in the summer and darker in the winter, with a light colored mark on the throat. There are also two darker bands on their flanks.
In the summer, the Apennine chamois prefers rock faces and pasture lands at heights above 1700 meters for its habitat, and in the winter it prefers to retreat to the woods below. Diet of the chamois consists of grasses, leaves, buds, shoots and fungi. Adult males prefer a solitary life, only approaching females during the mating season. Groups consist only of females, young males, and "kids." Females give birth to only one kid after a gestation period of 23 to 24 weeks.[3]
A 2014 study by Durham University discovered that these goats are shrinking in size due to global warming and climatic changes.[4]
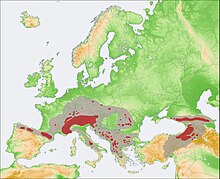 Range of Rupicapra during the Holocene (grey) and present range (red)
Range of Rupicapra during the Holocene (grey) and present range (red) Rupicapra is a genus of goat-antelope called the chamois. They belong to the bovine family of hoofed mammals, the Bovidae.
Two extant species are recognized.
The Apennine chamois (Rupicapra pyrenaica ornata) is a subspecies of the Pyrenean chamois, a goat-like mammal found in the mountains of Europe. Both male and female have hook-shaped horns that slightly curl backwards and grow little by little each year, never falling off. Their coats are light brown in the summer and darker in the winter, with a light colored mark on the throat. There are also two darker bands on their flanks.
In the summer, the Apennine chamois prefers rock faces and pasture lands at heights above 1700 meters for its habitat, and in the winter it prefers to retreat to the woods below. Diet of the chamois consists of grasses, leaves, buds, shoots and fungi. Adult males prefer a solitary life, only approaching females during the mating season. Groups consist only of females, young males, and "kids." Females give birth to only one kid after a gestation period of 23 to 24 weeks.
A 2014 study by Durham University discovered that these goats are shrinking in size due to global warming and climatic changes.